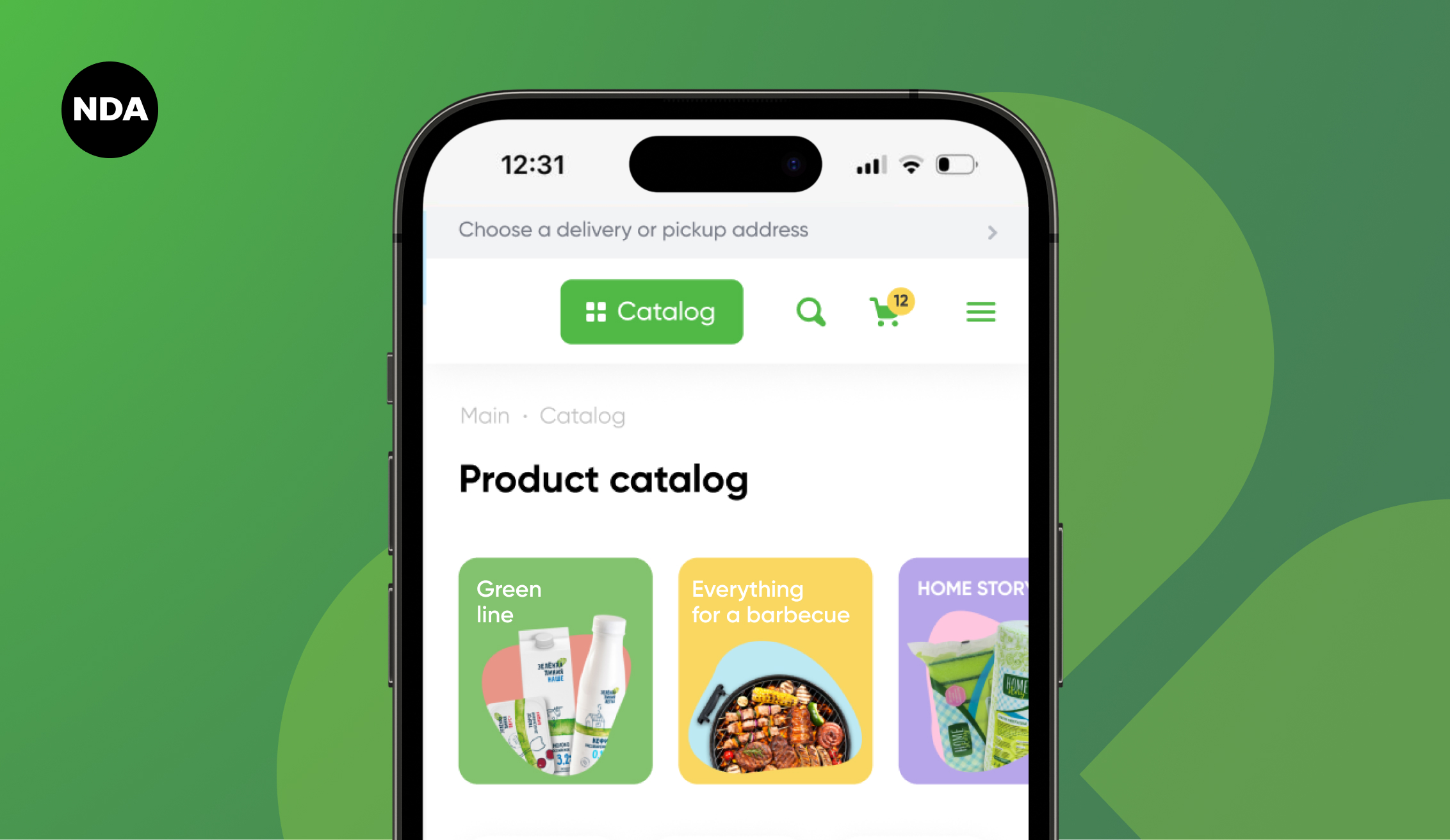
In the digital product landscape, creating a successful product demands an intricate understanding of the user's journey. This includes target audience analysis, prototype creation and rigorous solution testing. Central to this process is the thoughtful selection of fonts, color palettes, element sizes, and graphic details. These components form the foundation of both UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design.
What is UX Design?
User Experience or UX design focuses on optimizing the user's interaction with a product. It aims to solve critical issues concerning user convenience, impression, and goal achievement. For example, a UX designer evaluates how simple it is for users to order a taxi, have food delivered, or apply for a credit card online via a digital product.
Key roles of a UX designer include:
-
Analyzing competitors
-
Researching the target audience
-
Mapping out business processes
-
Conducting usability tests and in-depth interviews to capture user reactions
-
Exploring user psychology, motivations, and behavioral patterns
-
Creating Customer Journey Maps (CJM)
-
Designing an intuitive interface layout
Consider a user flow for a project like "Junk a Car" as an example.
What is UI Design?
UI design focuses on the visual aesthetics of a user interface. A UI designer's role is to make the interface visually appealing and functionally expressive.
Their roles include:
-
Selecting appropriate color schemes, fonts, and sizes for elements
-
Designing animations and static elements like images, tables, buttons, sliders, and forms
-
Developing a cohesive brand identity, UI kits, and design systems
-
Adapting all interface elements for compatibility with different devices
An example is the design of a product card for the SYNERGETIC online store, which blends traditional e-commerce aesthetics with client-specific preferences.
Distinguishing Between UX and UI
While UX design focuses on the logical function of an interface, UI design is concerned with its visual aspects. These disciplines, though distinct, are deeply interconnected and often inseparable in practice. In some companies, these roles are divided; a UX designer starts with research and prototyping, while a UI designer brings these prototypes to life visually. However, many professionals today manage both UX and UI tasks, overseeing everything from initial research to the creation of the final versions of graphical elements.
Applications of UX and UI
UX and UI design are commonly linked to digital interfaces such as e-commerce platforms, banking systems, corporate websites, mobile applications, and various online services. Yet, the principles of UX/UI can be found in the non-digital, physical world around us, from the design of a car's dashboard to the layout of the buttons found on an espresso machine.
Principles of Effective UX/UI Design
-
Usefulness: Products should solve real problems effectively without introducing unnecessary complexity or distractions.
-
Convenience: A well-designed interface uses familiar icons and logical placements to help users quickly understand and interact with the system.
-
Consistency: Users should recognize and understand the product across various parts of the interface, necessitating a consistent design across all components.
-
Accessibility: Products should accommodate all users, including those with visual impairments, by offering adaptable features such as voice input and dark display modes.
In summary, UX and UI are critical, yet distinct aspects of product design. Their seamless integration is essential for crafting digital products that are not only visually appealing but also provide a smooth and enjoyable user experience.